Exploring Human Centered Design: Enhancing User Experience through Empathy
Diving into the realm of human-centered design, this introduction sets the stage for a captivating journey through the principles and practices that prioritize the needs and behaviors of users. From innovative design processes to impactful outcomes, the world of human-centered design awaits exploration.
Human-centered design is not just about creating products or services; it's about understanding the core of human interaction with design. Let's unravel the layers of empathy, user research, and iterative design that shape this dynamic field.
Definition of Human-Centered Design
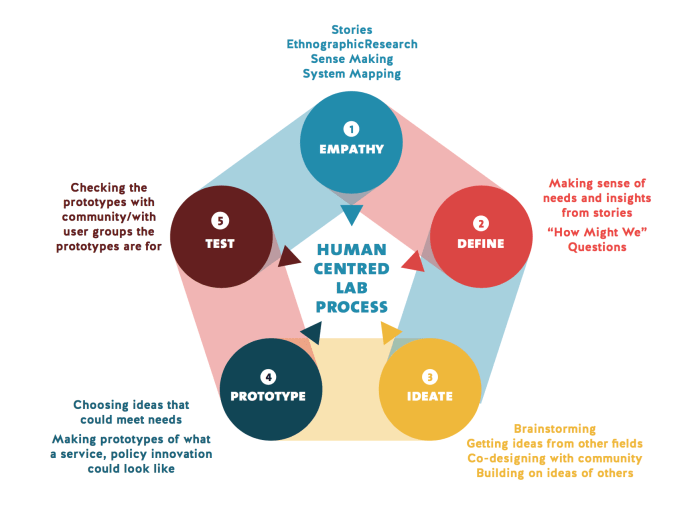
Human-centered design is an approach to creating products, services, or systems that focuses on the needs, behaviors, and preferences of the end-users. It involves empathizing with users, defining their problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing to ensure the final outcome meets user expectations and enhances user experiences.Considering human needs and behaviors in design processes is crucial as it ensures that the final product or service is intuitive, user-friendly, and addresses the actual needs of the target audience.
By incorporating user feedback and involving users throughout the design process, human-centered design helps in creating solutions that truly resonate with the end-users.
Examples of Human-Centered Design Impact
- Apple's iPhone: Apple revolutionized the smartphone industry by focusing on user experience and design aesthetics. The intuitive interface, simple navigation, and user-centric features of the iPhone have set new standards for mobile devices.
- Tesla's Electric Vehicles: Tesla's electric vehicles are designed with a focus on user comfort, convenience, and sustainability. The seamless integration of technology, user-friendly interfaces, and innovative features have made Tesla a leader in the electric vehicle market.
- Airbnb's Platform: Airbnb's platform connects travelers with unique accommodations around the world, offering personalized experiences based on user preferences. By considering user feedback and preferences, Airbnb has revolutionized the travel industry and redefined the concept of hospitality.
Principles of Human-Centered Design
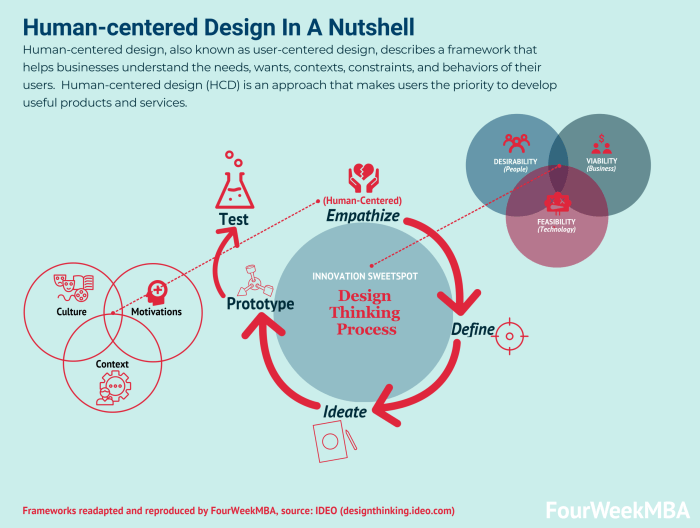
Human-centered design is guided by several key principles that focus on putting the needs and experiences of users at the forefront of the design process. By following these principles, designers can create products and solutions that truly resonate with the intended users.
Empathy as a Crucial Element
Empathy is a fundamental aspect of human-centered design as it involves putting oneself in the shoes of the users to understand their needs, challenges, and motivations. By empathizing with users, designers can gain valuable insights that inform the design process and lead to solutions that address real-world problems effectively.
Iterative Design and User Feedback
Iterative design is another essential principle of human-centered design, emphasizing the importance of continuous refinement and improvement based on user feedback. Designers create prototypes and gather feedback from users to make incremental changes, ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the users.
This iterative approach allows for flexibility and adaptability throughout the design process, leading to more user-centric solutions.
User Research in Human-Centered Design
User research is a crucial aspect of human-centered design as it involves understanding the needs, behaviors, and preferences of the end-users. By gathering insights directly from users, designers can create solutions that truly meet their requirements and enhance user experience.
Significance of Conducting User Research
User research helps in uncovering valuable information that guides the design process. It ensures that the final product or service is tailored to the users' needs, leading to higher satisfaction and usability. By empathizing with users and involving them in the design process, designers can develop more meaningful and effective solutions.
- Interviews: Conducting one-on-one interviews with users to gather in-depth insights into their thoughts, preferences, and pain points.
- Surveys: Distributing surveys to a larger group of users to collect quantitative data on their preferences and behaviors.
- Observation: Observing users in their natural environment to understand how they interact with products or services.
- Usability Testing: Testing prototypes with real users to identify usability issues and gather feedback for improvements.
Examples of User Research Influencing Design Decisions
During user testing, it was revealed that most users struggled to find the checkout button on the website. This feedback led to a redesign of the interface, resulting in a significant increase in conversion rates.
- By conducting interviews with elderly users, a smartphone design team discovered the need for larger fonts and simplified navigation, leading to a more accessible user interface.
- Through observation sessions at a hospital, designers noticed that nurses often had difficulty locating medical supplies. This insight led to a redesign of the storage system for better efficiency.
Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping and testing are crucial aspects of human-centered design, as they allow designers to gather feedback from users early on in the design process. This iterative approach helps in creating solutions that truly meet the needs and preferences of the target users.
Importance of Prototyping
Prototyping helps in visualizing ideas, gathering feedback, and testing assumptions before investing significant time and resources in the final product. It allows designers to quickly iterate on different design concepts and refine them based on user input. By creating tangible representations of ideas, designers can better communicate their vision and ensure alignment with user expectations.
- Prototypes help in identifying usability issues early on, saving time and resources in the long run.
- They facilitate collaboration among team members and stakeholders by providing a tangible reference point for discussions.
- Prototyping encourages creativity and innovation by allowing designers to explore multiple design options and iterate on them rapidly.
Steps to Create Effective Prototypes for Testing
Creating effective prototypes involves the following steps:
- Define the prototype's purpose:Clearly Artikel what you want to achieve with the prototype and what specific aspects you want to test.
- Choose the right fidelity:Decide on the level of detail and functionality needed for the prototype based on the stage of the design process.
- Iterate and refine:Continuously iterate on the prototype based on user feedback, making improvements and refinements as necessary.
- Test with real users:Conduct usability testing with real users to gather feedback on the prototype's effectiveness and usability.
Iterative Process of Testing and Refining Prototypes
The iterative process of testing and refining prototypes involves:
- Collecting feedback:Gather feedback from users through usability testing, interviews, surveys, or observations.
- Analyzing feedback:Evaluate the feedback received to identify trends, pain points, and areas for improvement.
- Implementing changes:Make necessary changes to the prototype based on the feedback received, focusing on improving user experience.
- Testing again:Repeat the testing process with the updated prototype to validate the changes made and gather additional feedback.
Final Thoughts
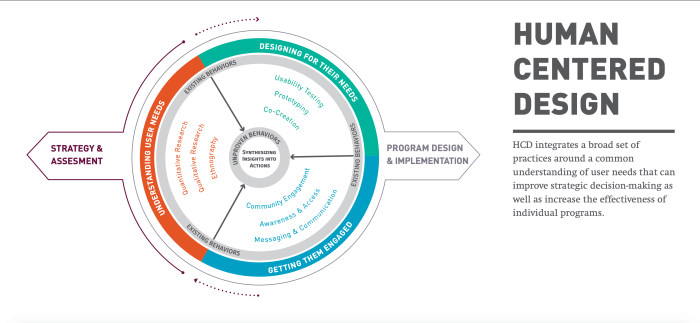
As we conclude this insightful discussion on human-centered design, we reflect on the power of putting users at the heart of the design process. By embracing empathy, iteration, and user feedback, we pave the way for transformative solutions that resonate deeply with people's needs and desires.
FAQ Guide
How does human-centered design differ from traditional design approaches?
Human-centered design focuses on understanding user needs and behaviors to create solutions that truly resonate with them, while traditional design may prioritize aesthetics or technical aspects.
Why is empathy considered a cornerstone of human-centered design?
Empathy allows designers to step into the shoes of users, gaining deeper insights into their experiences, motivations, and challenges, ultimately leading to more empathetic and effective design solutions.
What role does user research play in human-centered design?
User research helps designers gather valuable insights about users' preferences, pain points, and behaviors, guiding design decisions to create more user-centric solutions.




